Data Security Learning Module
Basic concepts in Data Security
Created By Eng. Eslam Osama
1. Basic Concepts in Data Security
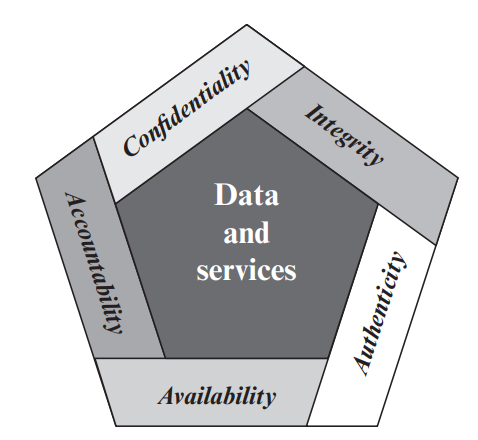
The practice of protecting digital information from unauthorized access, corruption, or modification.
It refers to our ability to protect our data from those who are not authorized to view it and accessible only to authorized individuals.
It refers to the ability to prevent our data from being changed in an unauthorized or undesirable manner during storage or transmission.
Ensuring that data and resources are accessible to authorized users when needed.
2. Security Threats
Threats to Confidentiality
Individuals who use technical skills to break into systems, exploit vulnerabilities, or steal data.
Individuals who pretend to be someone else (an authorized user) to gain access to systems or data.
Individuals or entities who try to access systems, data, or resources without proper permission or authorization.
Downloading files or software from the internet without proper security measures, such as encryption, verification, or scanning for malware.
Short for malicious software and is like any software, but intentionally designed to harm, exploit, or compromise systems, networks, or data.
Threats to Availability
Deliberate actions by individuals to disrupt systems, data, or resources, making them unavailable.
Accidental actions by individuals that lead to systems, data, or resources becoming unavailable.
Events or issues not caused by humans that disrupt systems, data, or resources, making them unavailable.
3. Authentication & Authorization
The process of verifying the identity of a user, system, or device to ensure they are who they claim to be. Purpose is to prevent unauthorized access to system, data, or resources.
Common Authentication Techniques
Users provide a username and password to prove their identity.
Requires two forms of verification which are something you know (password) and something you have (a code sent to your phone).
Uses unique physical characteristics to verify identity, such as fingerprints, facial recognition, or voice patterns.
An encrypted piece of data which contains information about its owner, issuer of certificate, and some other data.
Granting or denying access to specific resources based on a user's identity and permissions.
Means making sure that people are responsible for their actions and can be identified if something goes wrong. It's about tracking who did what, so actions are traceable and answerable.
4. Security Attacks
| Aspect | Threat | Attack |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | A potential danger that could exploit a vulnerability in a system | The actual attempt to harm or exploit a system |
| Nature | Possibility of harm | Action of causing harm |
| Example | A hacker planning to steal data from a company's database | The hacker actually breaking into the database and stealing data |
Types of Security Attacks
The attacker observes or monitors the system but does not alter or disrupt it. The goal is usually to gather information without being detected.
- Packet Sniffing: A hacker captures data packets being sent over a network (like passwords or emails) but doesn't interfere with the communication.
- Traffic Analysis: Traffic analysis involves studying the patterns of network traffic (e.g., who is communicating, when, how often, and how much data is being sent) without necessarily looking at the content of the packets.
Key Point: Passive attacks are hard to detect because they don't change the system.
The attacker interacts with or modifies the system. The goal is to disrupt, alter, or damage the system or data.
- Denial of Service (DoS): A hacker floods a website with traffic to crash it, making it unavailable to users.
- Man-in-the-Middle (MITM): A hacker intercepts and alters communication between two parties without their knowledge.
Key Point: Active attacks are easier to detect because they cause noticeable changes or disruptions.
5. Important Terminologies
The original, readable message or data before it is encrypted.
The scrambled, unreadable version of the plaintext after encryption.
A piece of information (like a code) used to encrypt or decrypt data.
A method or algorithm used to encrypt plaintext into ciphertext or decrypt ciphertext back into plaintext.
The process of converting plaintext into ciphertext to protect its confidentiality.
The process of converting ciphertext back into plaintext so it can be read.
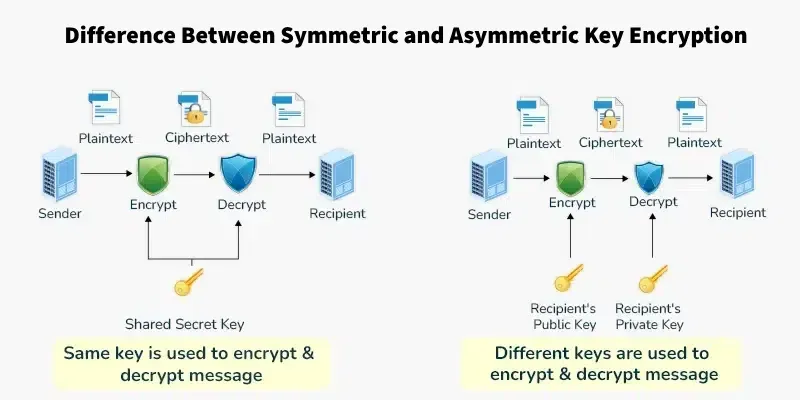
A type of encryption where the same key is used to encrypt and decrypt data.
A type of encryption that uses two different keys: a public key to encrypt and a private key to decrypt.
A key that is shared publicly and used to encrypt data.
A secret key that is kept private and used to decrypt data.